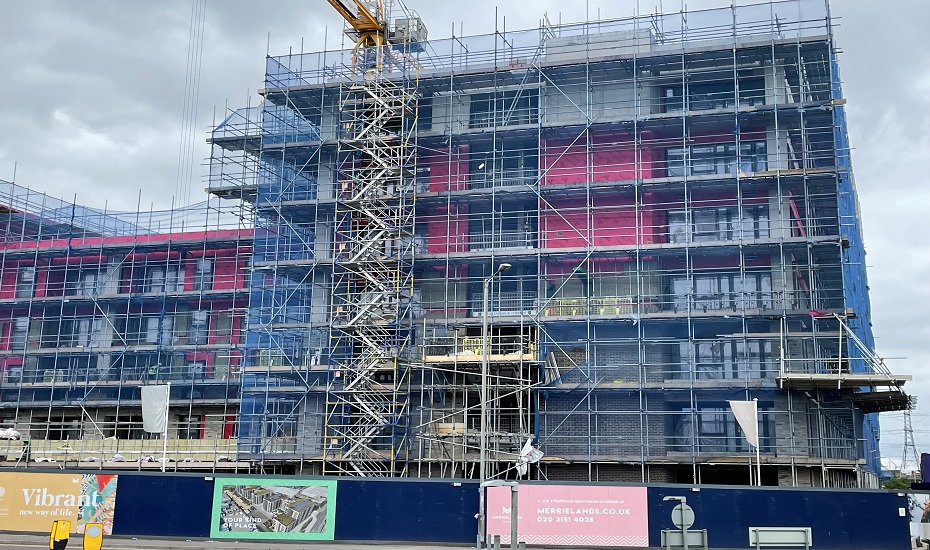
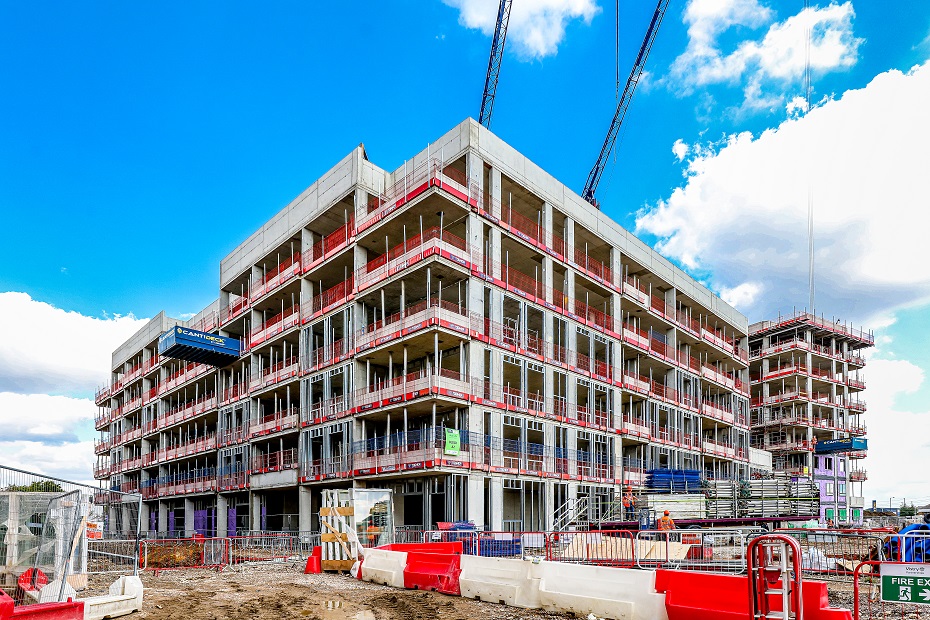
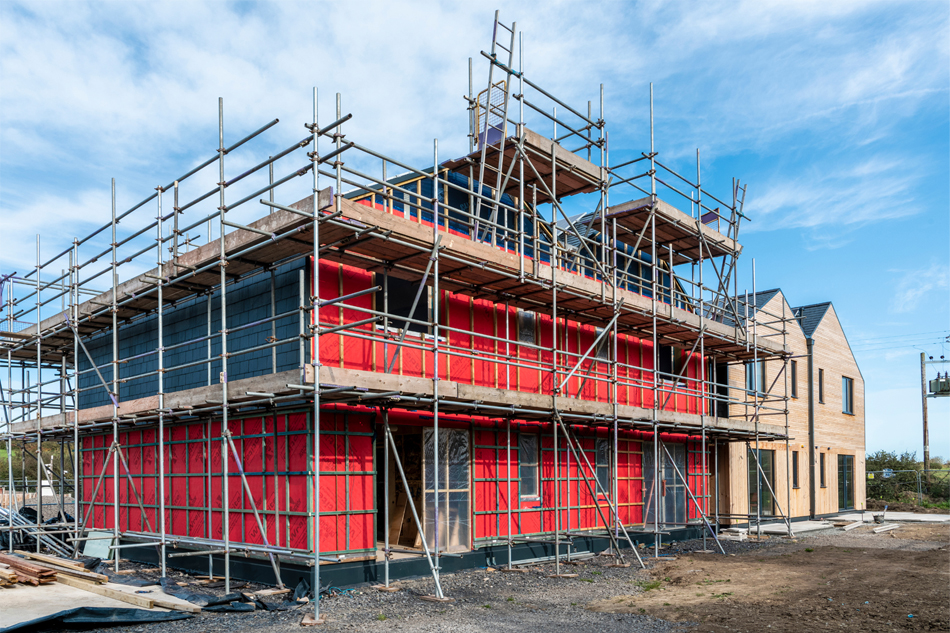
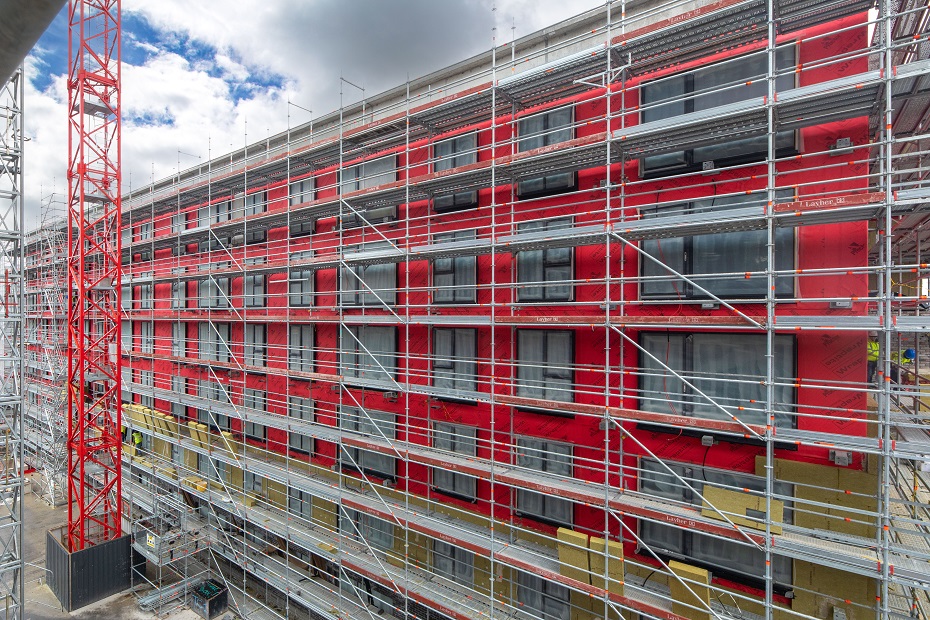
A four-acre site, originally part of the Ford Dagenham car plant, will provide a new home for 325 residential units in a series of five to ten storey apartment buildings. The Merrielands Crescent project is part of the London Riverside Opportunity Area, a 3,000-hectare regeneration zone designated in the London Plan for up to 26,500 homes across the borough of Barking & Dagenham.
The construction of the Merrielands development is managed by Inland Partnerships, on behalf of Clarion Housing Group, the UK’s largest housing association.
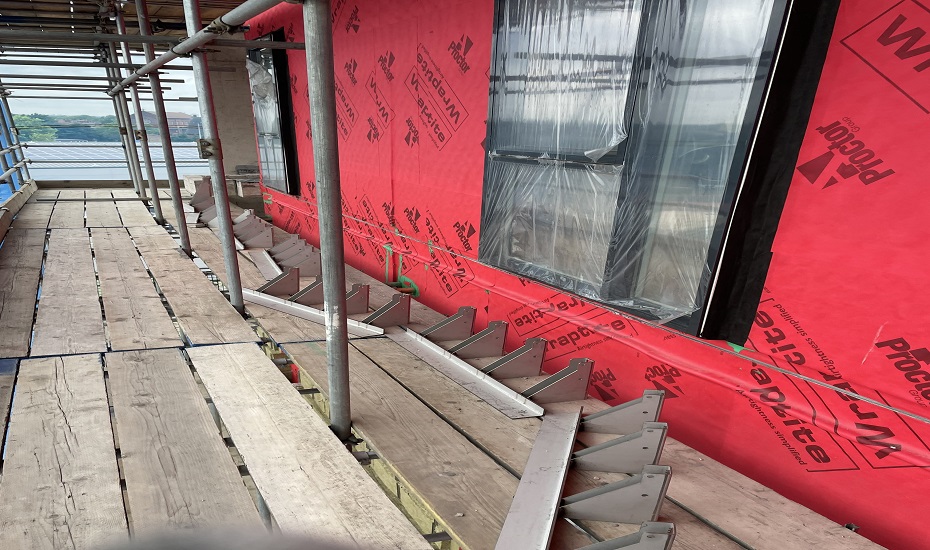
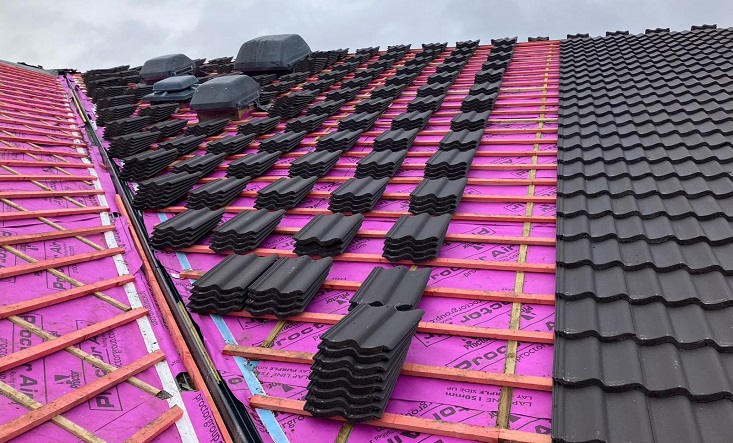
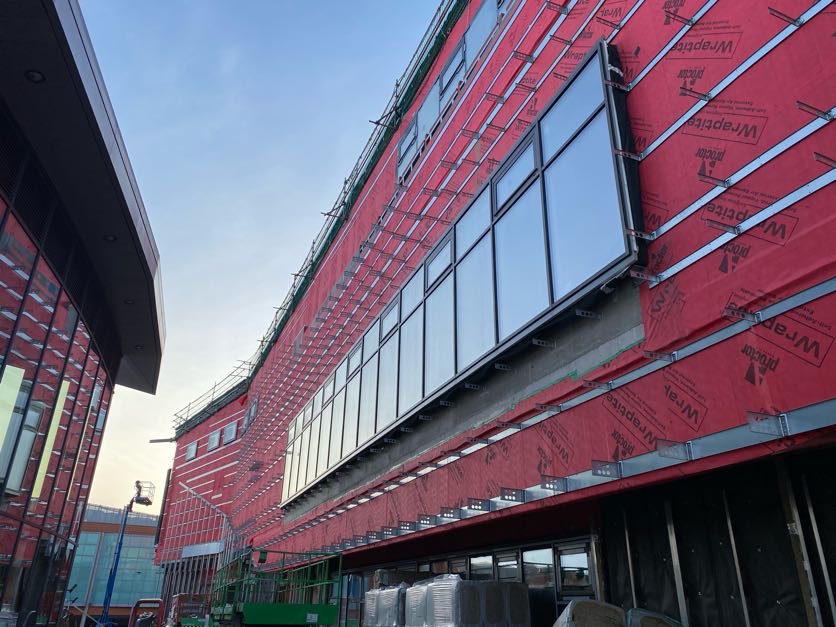
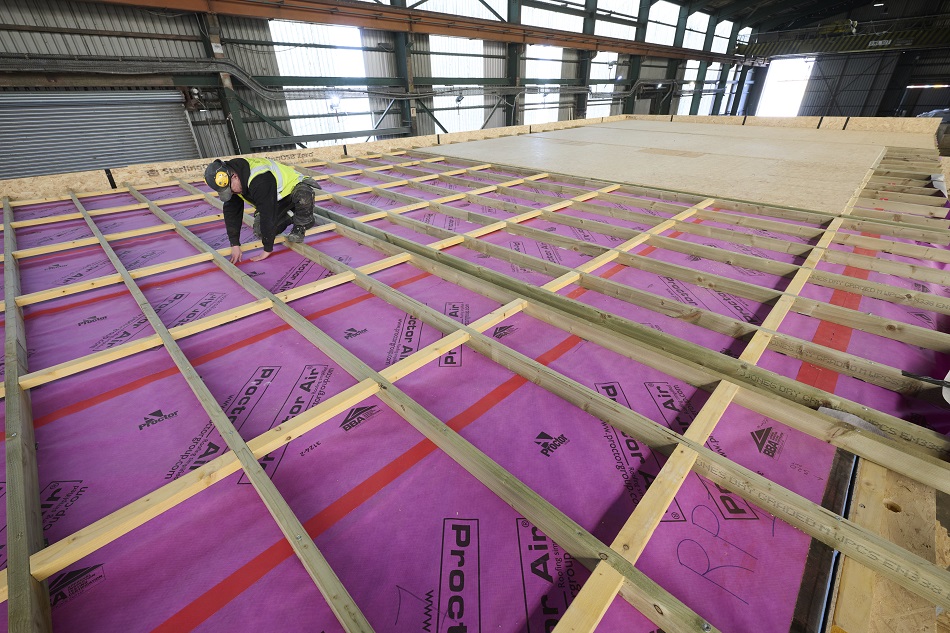
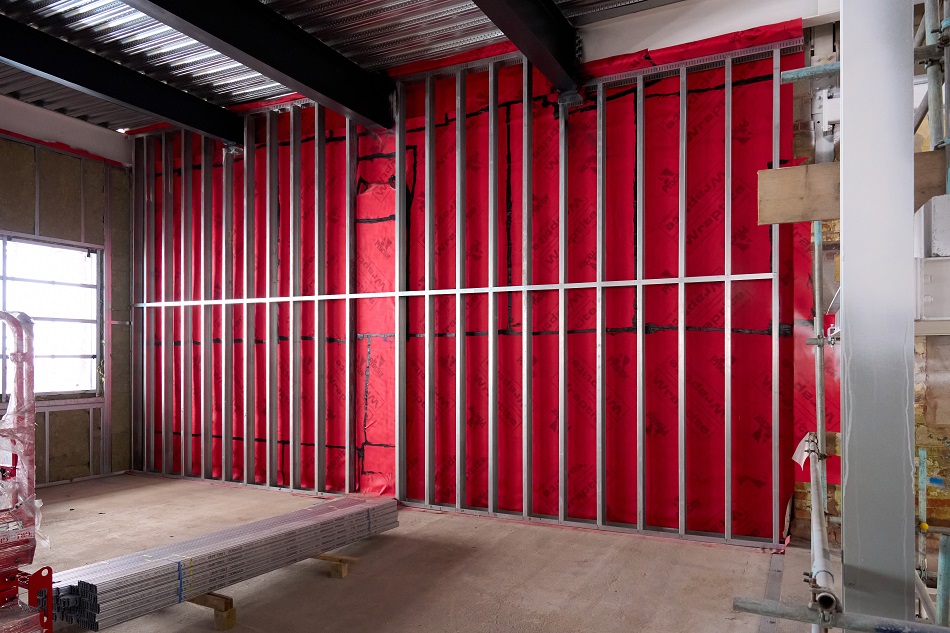
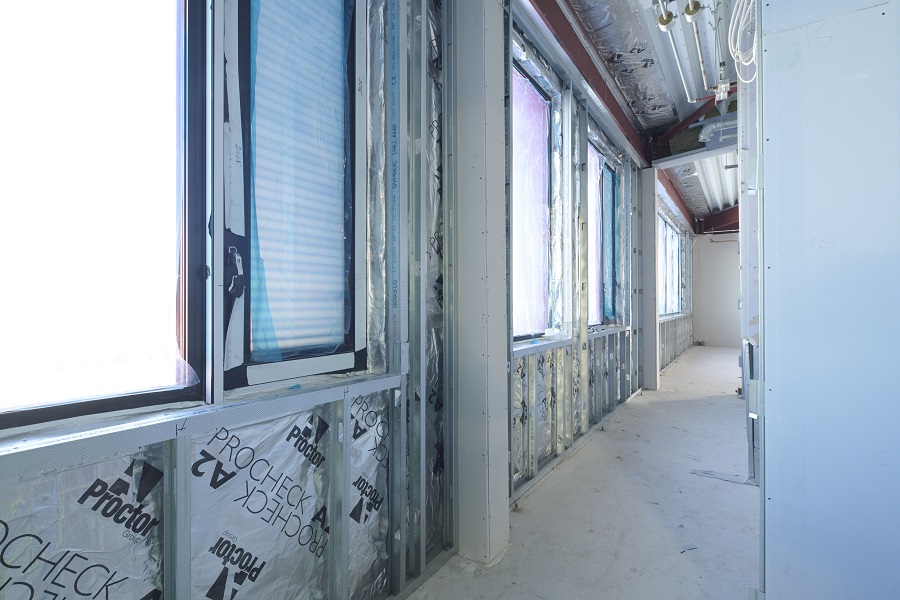
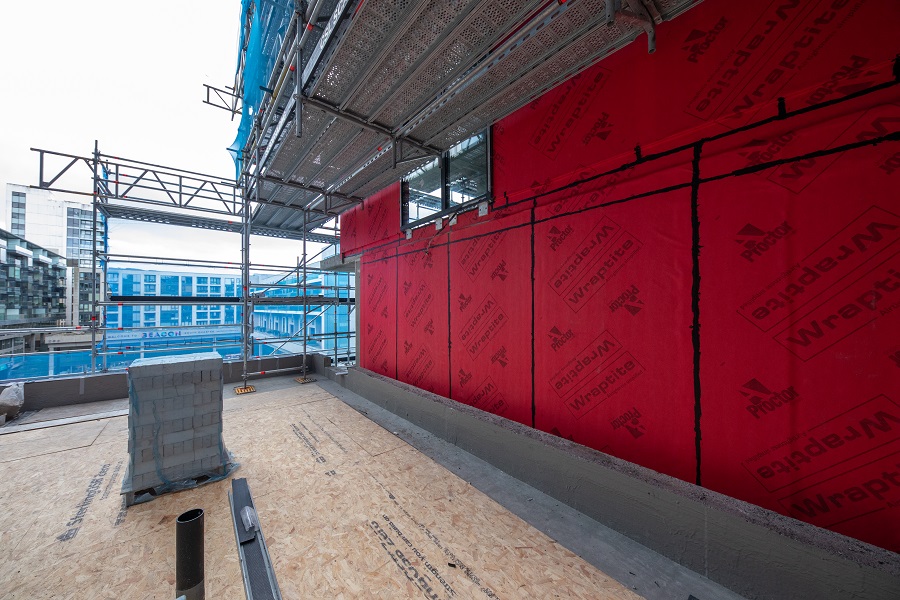
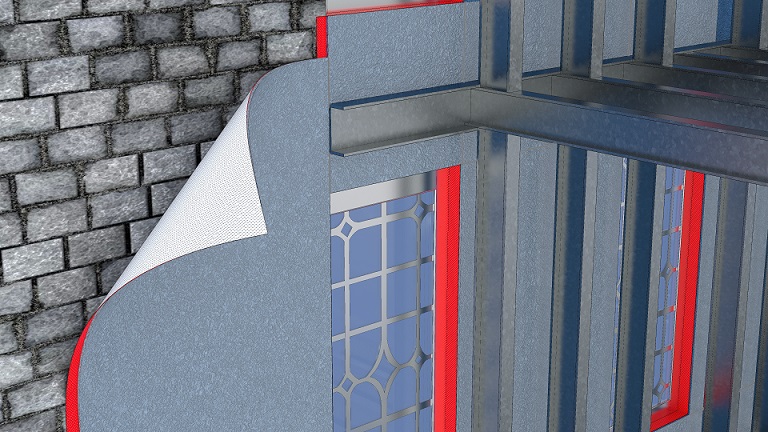
15,000m2 of the Wraptite® airtightness membrane from the A. Proctor Group features in the design. Wraptite is the only self-adhering vapour permeable air barrier certified by the BBA and combines the critical properties of vapour permeability and airtightness in one self-adhering membrane.